** 39.4 C to F: Converting Body Temperature **
39.4 c to f –
39.4 C to F: Ever wondered what a slightly elevated body temperature feels like in Fahrenheit? It’s a common question, especially when dealing with health concerns or simply understanding global temperature scales. While Celsius is the standard in many parts of the world, Fahrenheit is still used in the US and a few other countries.
Understanding how to convert between these scales is essential for communication and accurate measurement.
This guide will take you through the process of converting 39.4 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, explaining the underlying formula and its application in various contexts. We’ll also explore the significance of this temperature in human health, weather, and scientific experiments, comparing it to common temperature ranges experienced globally.
Get ready to dive into the world of temperature conversion!
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit: 39.4 C To F
Celsius and Fahrenheit are the two most common temperature scales used around the world. While they both measure temperature, they differ in their starting points and the size of their degree units.
History of Celsius and Fahrenheit
The development of these scales is rooted in historical context and scientific advancements.
- Celsius:Developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742, the Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Zero degrees Celsius (0°C) represents the freezing point of water, and 100 degrees Celsius (100°C) represents the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure.
The scale is divided into 100 equal intervals, each representing one degree Celsius.
- Fahrenheit:Invented by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, the Fahrenheit scale is based on a different set of reference points. Zero degrees Fahrenheit (0°F) was initially defined as the temperature of a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride.
Fahrenheit later adjusted the scale, setting 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as the boiling point of water. The scale is divided into 180 equal intervals, each representing one degree Fahrenheit.
Countries and Regions Using Each Scale
The use of Celsius and Fahrenheit varies across the globe.
- Celsius:The Celsius scale is the primary temperature scale used in most countries around the world, including those in Europe, Asia, Africa, South America, and Australia. It is also used in scientific research and international organizations.
- Fahrenheit:The Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States, the Bahamas, Belize, and a few other countries. It is also commonly used in some industries, such as aviation.
Applications of Temperature Conversion
Temperature conversion plays a vital role in various fields, ensuring accurate measurements and facilitating communication across different systems. Understanding how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial for professionals in medicine, engineering, and meteorology, among others.
Importance in Medicine
Accurate temperature conversion is essential in medicine for patient care and diagnosis. Medical professionals use thermometers to measure body temperature, which is typically expressed in degrees Celsius. However, some medical devices and literature might use Fahrenheit.
- For instance, a doctor might need to convert a patient’s temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit to compare it with a standard reference range.
- Similarly, medical professionals need to be able to convert temperatures when administering medications or performing procedures.
Importance in Engineering
Engineers rely on temperature conversion for designing and building structures, machines, and systems. Many engineering specifications and standards use Fahrenheit, while others use Celsius.
- For example, engineers working on a construction project might need to convert temperatures to ensure the materials used can withstand the expected temperature ranges.
- In manufacturing, temperature conversion is crucial for controlling processes such as heat treatment, where precise temperature control is critical for achieving desired properties in materials.
Importance in Meteorology
Meteorologists use temperature conversion to understand and communicate weather patterns and forecasts. While most countries use Celsius for reporting temperatures, some still use Fahrenheit.
- For example, meteorologists might need to convert temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit to compare data from different sources or to provide forecasts in regions where Fahrenheit is the standard unit.
- Temperature conversion is also essential for understanding and interpreting weather data, such as temperature gradients and the impact of temperature changes on weather phenomena.
Examples of Real-World Scenarios
- A traveler visiting the United States from a country that uses Celsius might need to convert the temperature forecast to understand the weather conditions.
- A chef might need to convert a recipe’s temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius to ensure the dish is cooked properly.
- A mechanic might need to convert the temperature reading on a car’s engine to Celsius to troubleshoot an overheating issue.
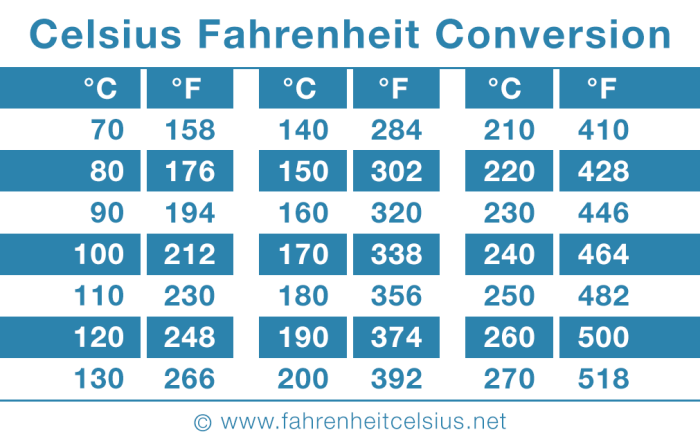
Common Benchmarks, 39.4 c to f
The following table illustrates the temperature conversion of common benchmarks:
| Benchmark | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Freezing Point of Water | 0 | 32 |
| Boiling Point of Water | 100 | 212 |
| Average Human Body Temperature | 37 | 98.6 |
Epilogue
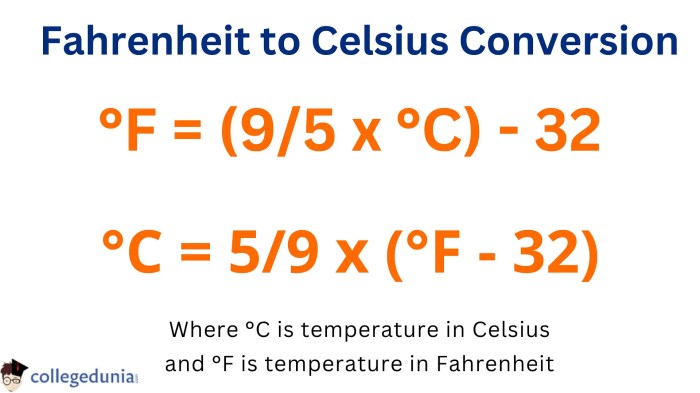
So there you have it – 39.4 degrees Celsius converts to a slightly above-average body temperature of 103 degrees Fahrenheit. While this might seem like a small difference in numbers, it highlights the importance of understanding temperature conversion, especially in fields like medicine, engineering, and meteorology.
Next time you encounter a temperature reading in a different scale, remember the simple formula and tools available to make the conversion seamless. And don’t forget, understanding these scales helps us navigate the world around us with greater accuracy and clarity.